Mobile Suit Gundam
It won’t work
Last
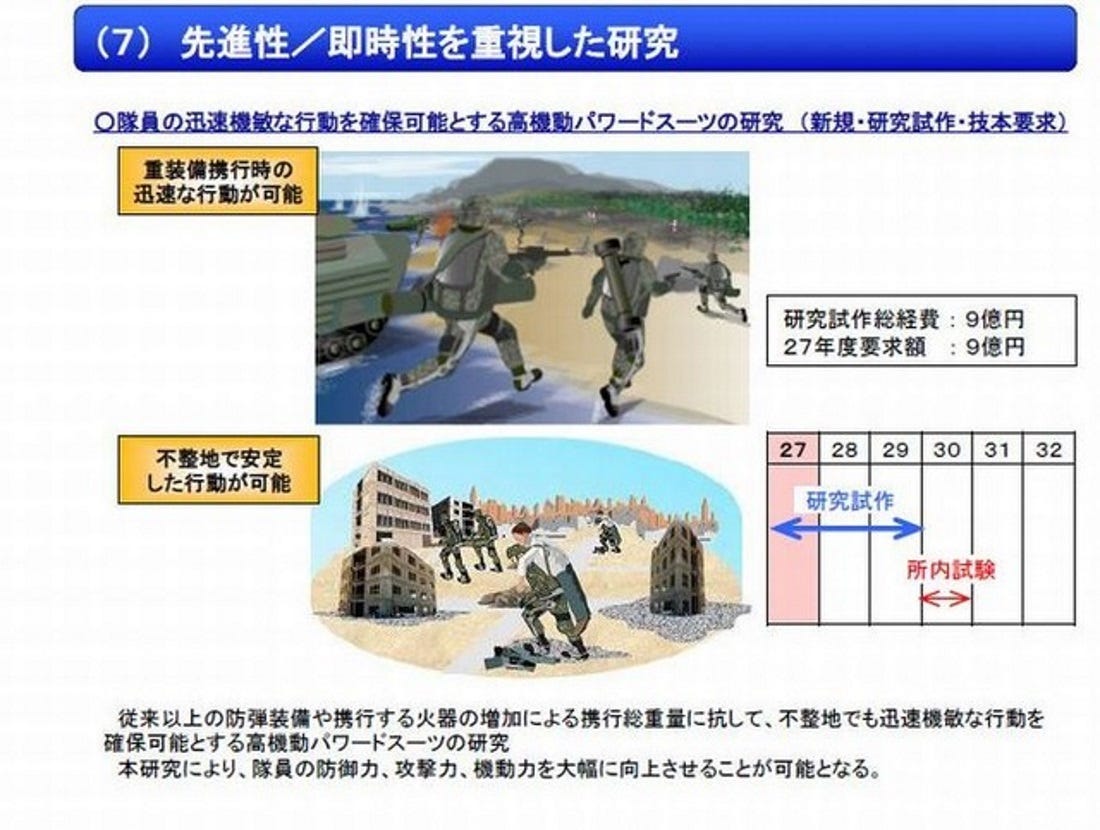
December, Japan’s defense research organization proposed allocating
$7.5 million of its 2015 budget towards research into “highly mobile
powered suits.”
Which sounds awesome. If anyone can craft Iron Man
style robotic armor, it’s Japan, right? Don’t hold your breath. As the
U.S. military has learned, exoskeletons are still a long way from the
battlefield.
The machines are a staple of science fiction films such as Elysium, Edge of Tomorrow and Avatar. Since we’re talking about a Japanese project, we’d be remiss to leave out Mobile Suit Gundam.
And like Ripley’s power loader at the end of Aliens, powered suits are a dual-use technology—meaning they have both civilian and military applications.
But to dial the concept away from science fiction and back to reality, it’s a fairly simple concept. In short, power-assisted robotic suits decrease fatigue while increasing strength.
The
ability to lift and manipulate heavy loads—like a wearable
forklift—could make exoskeletons ideal for reducing occupational
hazards. Warehouse, shipyard and construction workers could use them for
jobs that involve moving heavy objects.
Soldiering
is physically demanding work, and exoskeletons could reduce battlefield
fatigue and enhance a soldier’s speed and endurance. The dual
military-civilian nature of the technology is also a perfect match—in
theory—for Japan’s Self-Defense Forces.
Tokyo
has a defensive-oriented military, and regularly deploys troops for
disaster relief missions. Japan sent soldiers to help rescue its
citizens after the 2011 earthquake and tsunami, and last year’s volcanic eruption in Nagano.
In
addition to helping out during large-scale disasters, local governments
often request military assistance to help rescue people buried by heavy
snow and landslides. These first responders have to lift heavy debris
in terrain often left inaccessible to rescue vehicles.
But
fatigue is the main problem for the troops, who must rush out to find
missing and injured people. Time is absolutely crucial in rescue
operations, and machine-assisted endurance could make the difference
between whether someone lives or dies.
If Japan were to go to war, the exoskeletons would be a “force multiplier,” in military terms. An enemy’s superior numbers might not matter much if Tokyo’s troops wear power armor.
Japan’s
Technical Research and Development Institute—part of the ministry of
defense—has worked on the technology since 2010 as part of its “Zero
Casualty Battle System” concept. The idea is to avoid human casualties
by replacing soldiers with tech whenever possible.
A
powered suit could carry stronger bulletproof protection against enemy
fire without sacrificing speed and mobility — a problem associated with
ceramic plate and Kevlar.
The
question is whether Japan presses ahead and attempts a full-body
exoskeleton, or a simpler lower-body frame. The former probably isn’t
practical—owing to the technical demands. But a partial suit wouldn’t
provide much strength, though it could give the wearer more agility and
endurance.
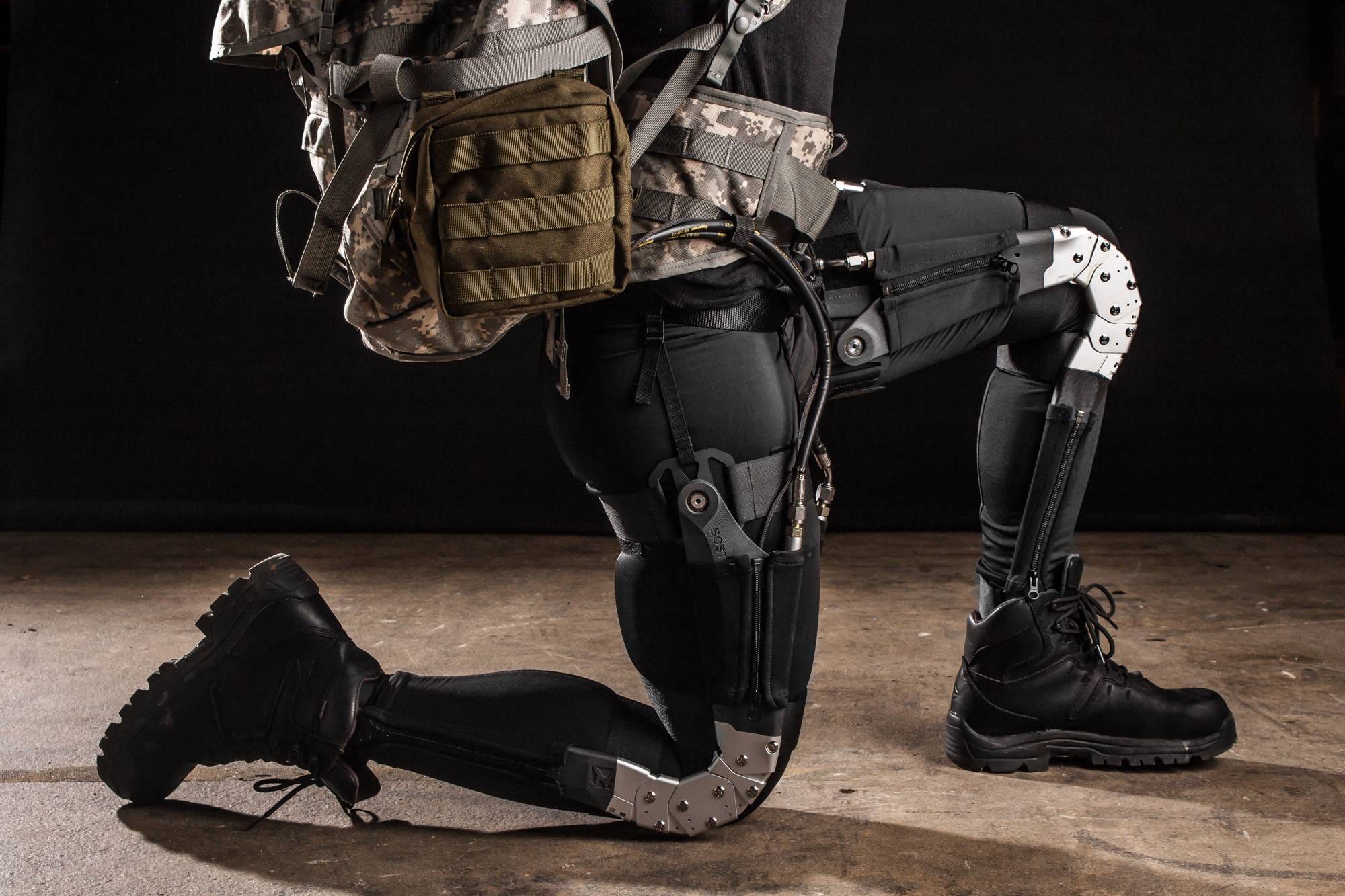
Japanese military researchers have already constructed a pair of robotic exoskeletons for the lower body that might one day allow a user to dash and leap around with greater power and speed.
But
supplying power is still a problem, and Tokyo’s prototypes all require
long cables. That’s fine for the laboratory, but using it in the field
would require an enormous battery—with current technologies.
While
the design of the suits could accommodate a bigger battery, it’s an
inefficient way to provide power. But energy concerns aren’t stopping
the research, and Tokyo’s program is already producing some cutting-edge
robotics.
At the Japanese
defense ministry’s 2012 Defense Technology Symposium, researchers
displayed one such technology—high-pressure elastic muscles fitted to a pair of robotic legs that could leap over a meter in less than a second.
But the major problem of every exoskeleton is energy. Putting aside the current limitations on battery tech — which researchers might overcome — they still require some kind of fuel to operate.
Sure, a lot of military hardware requires electricity, but robo-suits are different because a soldier wears them. What happens when the suit runs out of power with its operator still inside?
When
the exoskeleton dies, the actuators and elastic musculature will
increase resistance against the operator’s movement. If a soldier uses
the suit’s added strength to carry more equipment, then a dead suit
forces the soldier to ditch this additional kit.
If
the operator is strapped in, then it will take time to disengage from
whatever fixtures hold them into the frame. That’s time when the
operator is vulnerable. In a combat situation, getting stuck inside a
inert robot could mean death.
But America might have the answer. Just maybe.
Lockheed Martin and Ekso Bionics have a working system called HULC.
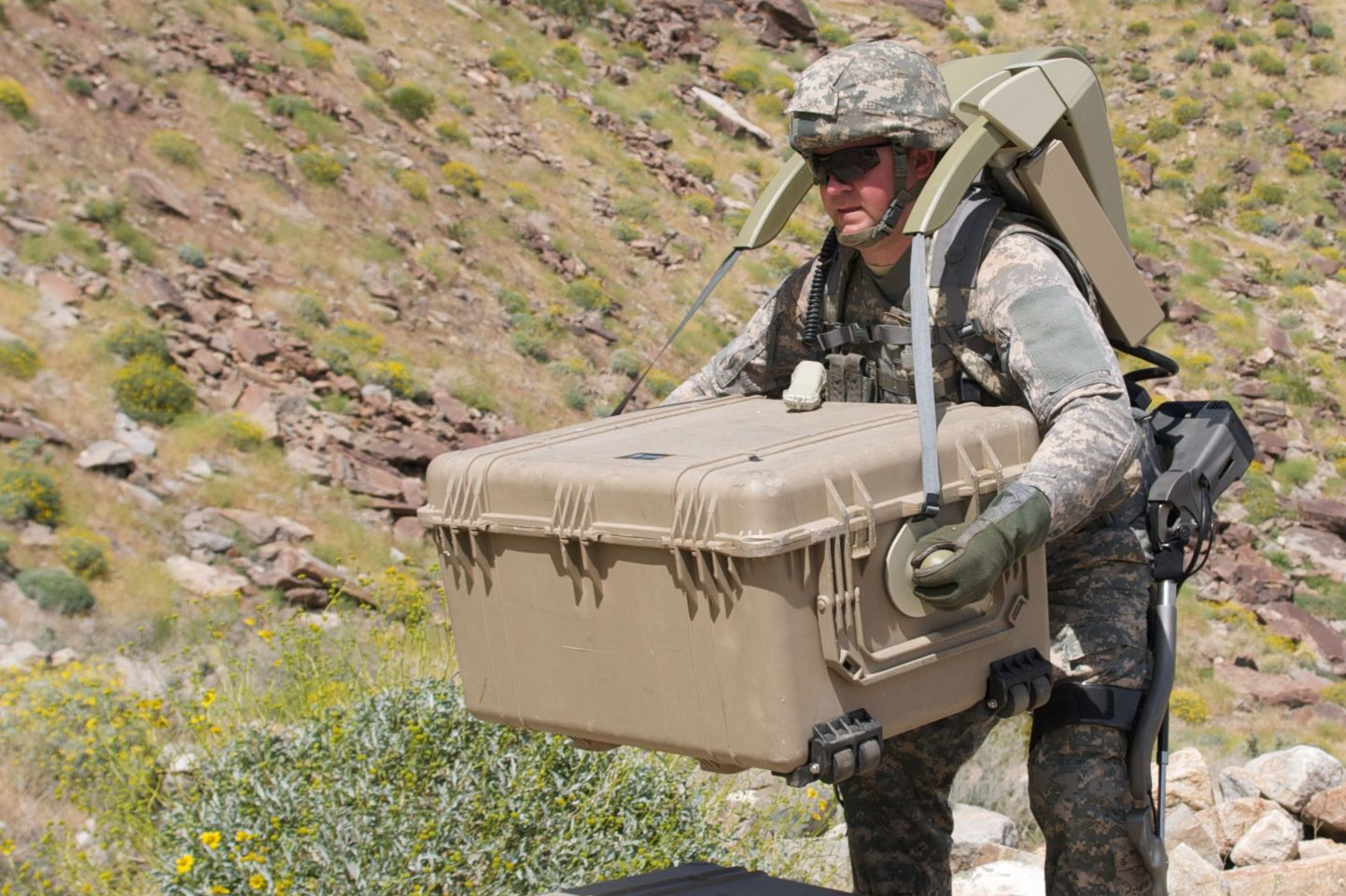


Lockheed Martin’s HULC suit. Lockheed Martin photo

HULC. (Photo by Lockheed Martin)
Dismounted warfighters often carry heavy combat loads that increase
the stress on the body leading to potential injuries. With a HULC
exoskeleton, these heavy loads are transferred to the ground through
powered titanium legs without loss of mobility.
The HULC is a completely un-tethered, hydraulic-powered anthropomorphic exoskeleton that provides users with the ability to carry loads of up to 200 pounds for extended periods of time and over all terrains. Its flexible design allows for deep squats, crawls and upper-body lifting.
An onboard micro-computer ensures the exoskeleton moves in concert with the individual. The HULC’s modularity allows for major components to be swapped out in the field. Additionally, its unique power-saving design allows the user to operate on battery power for extended missions. When battery power is low, the HULC system continues to support the loads and does not restrict mobility. HULC can also support a maximum load, with or without power.
Lockheed Martin is also exploring exoskeleton designs for industrial use and a wider variety of military mission specific applications. lockheedmartin.
The HULC is a completely un-tethered, hydraulic-powered anthropomorphic exoskeleton that provides users with the ability to carry loads of up to 200 pounds for extended periods of time and over all terrains. Its flexible design allows for deep squats, crawls and upper-body lifting.
An onboard micro-computer ensures the exoskeleton moves in concert with the individual. The HULC’s modularity allows for major components to be swapped out in the field. Additionally, its unique power-saving design allows the user to operate on battery power for extended missions. When battery power is low, the HULC system continues to support the loads and does not restrict mobility. HULC can also support a maximum load, with or without power.
Lockheed Martin is also exploring exoskeleton designs for industrial use and a wider variety of military mission specific applications. lockheedmartin.
The team is developing a long-range model—with fuel cells—sporting a
72-hour battery life. A titanium exoskeleton covers the lower-body and
back, carrying up to 200 pounds of equipment and allowing bursts of
speed at 10 miles per hour.
The
U.S. military didn’t buy HULC, but it funded work on a different Ekso
power suit—the Tactical Assault Light Operator Suit—for America’s
Special Operations Command.
Of all the programs underway, research into soft-skinned, super-light exoskeletons—such as TALOS—are the most promising.
Like a fighter pilot’s anti-G suit, soldiers could wear low-profile power-assisted skeletal frames under their existing uniforms.
Unlike hard-framed systems, DARPA’s Warrior Web
only aims to use small amounts of power — to provide a little extra
endurance. If ever deployed, it won’t provide much strength, but could
help reduce muscular injuries caused by the stresses of carrying heavy
equipment.

Tactical Assault Light Operators Suit (TALOS)
Iron Man Still Hollywood, Not Reality.
- Advanced Armor: Materials to support next generation full-body ballistic protection
- Mobility/Agility: Enhancement platforms such as powered exoskeletons
- Situational Awareness
- Light/noise discipline
- Command, Control, Communications & Computers (e.g., conformable and wearable antennae and wearable computers)
- Individual soldier combat ready displays including non-visual means of information display
- Power generation and management
- Thermal management of suit occupant
- Medical: Embedded monitoring and biomechanical modeling
These
systems would be more modest in comparison to the superhuman strength
and agility sought by Tokyo’s research program, but they could provide
an edge to soldiers without requiring huge amounts of power.
Then
there’s the cost. Japan’s $7.5 million in research and development on
the suit is a a fraction of the $80 million the U.S. is spending on
TALOS. And that’s nowhere near enough. “To do [TALOS] right, they need about a billion dollars,” an industry official told Military.com.
And
if the electricity goes out, it’ll still be a problem for any soldier
wearing one. That’s true for the U.S. military’s power suit projects and
it’s especially the case for Japan—if researchers go for a more radical, total-body exoskeleton.
by JAMES SIMPSON. medium.com

Post a Comment Blogger Facebook Disqus