
The breakthrough puts China one step ahead in the global race to harness a new, artificial kind of solar energy for clean and unlimited energy, the researchers claim. This has become a pressing concern as more of the earth’s natural reserves are rapidly depleting.
The experiment was conducted last week on a magnetic fusion reactor at the Institute of Physical Science in Hefei, capital of Jiangsu province, according to a statement on the institute’s website on Wednesday.
The reactor, officially known as the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), was able to heat a hydrogen gas - a hot ionised gas called a plasma - to about 50 million Kelvins (49.999 million degrees Celsius). The interior of our sun is calculated to be around 15 million Kelvins.
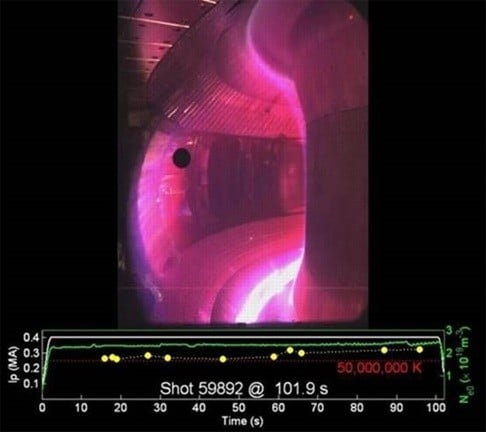 |
| A step closer to creating an artificial sun by heating hydrogen gas to 50 million Kelvins for a record time. Photo: Hefei Institute of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
According to this thermodynamic scale, absolute zero occurs at zero degrees (equivalent to minus 273.15 degrees Celsius), a point at which all molecular movement stops.
The temperature reached in Hefei was at the other end of the scale, and roughly the same as a mid-sized thermonuclear explosion. The goal of the experiment was to approximate the nuclear fusion conditions that occur deep inside the sun.
Although at least one other experiment in the last decade claims to have produced a hotter temperatures than this, it has never been duplicated and was unable to match the endurance - over one and a half minutes - of the Chinese test.
Meanwhile, physicists in Japan and Europe have been able to reach the same temperature as the Chinese team, but not for longer than a minute due to concerns of provoking a reactor meltdown.
The EAST was invented by Soviet scientists to control nuclear fusion for power generation.
 The
EAST tokomak device in Hefei. In order to ‘fuse’ two hydrogen atoms to
produce energy, it needs to heat the hydrogen plasma for 100 million
Kelvins. Photo: Chinese Academy of Sciences
The
EAST tokomak device in Hefei. In order to ‘fuse’ two hydrogen atoms to
produce energy, it needs to heat the hydrogen plasma for 100 million
Kelvins. Photo: Chinese Academy of SciencesAs a tokamak device, it uses a powerful magnetic field to confine plasma in the shape of a torus - imagine a large spinning doughnut -for safety reasons due to the phenomenally high temperatures being generated. The atoms are effectively held floating in place by superconducting magnets.
But controlling hydrogen gas in such a hot and volatile state is a formidable challenge, and one that most of the tokomak devices built over the last 60 years have not been able to sustain for more than 20 seconds.
The scientists in Hefei worked “day and night” to achieve the record level of endurance, according to the institute, which serves as a subsidiary of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The team claimed to have solved a number of scientific and engineering problems, such as precisely controlling the alignment of the magnet, and managing to capture the high-energy particles and heat escaping from the “doughnut”.
 Inside
the ‘doughnut’ (EAST). The metallic walls cannot come into direct
contact with the plasma or it will melt or evaporate immediately. The
scientists used a powerful magnetic field to keep the hot hydrogen gas
suspended in place. Photo: Chinese Academy of Sciences
Inside
the ‘doughnut’ (EAST). The metallic walls cannot come into direct
contact with the plasma or it will melt or evaporate immediately. The
scientists used a powerful magnetic field to keep the hot hydrogen gas
suspended in place. Photo: Chinese Academy of SciencesBut they still missed their mark, which was to reach 100 million Kelvins for over 1,000 seconds (nearly 17 minutes), they said, adding that it would still take years to build a commercially viable plant that could operate in a stable manner for several decades.
Unlike the process of nuclear fission that fuels thermal power stations around the world today by splitting the atoms of fissile materials such as uranium, fusion reactions work by “fusing” two light atomic nuclei - for example, two hydrogen atoms - together to release a huge amount of heat.
This can produce levels of energy three to four times greater than the results of nuclear fission. It also generate almost no radioactive waste.
The problem is the amount of heat created. Whereas nuclear fission only generates a few hundred degrees Celsius, fusion requires at least 100 million degrees Celsius (212 million degrees Fahrenheit).
A researcher involved with the EAST project said data from their experiment may be of use to the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) that is now under construction in France.
 A
colourised computer image shows the moment the first superhot plasma
was created in a separate experiment at the Wendelstein 7-X nuclear
fusion research centre at the Max-Planck-Institut for Plasma Physics
(IPP) in Greifswald, Germany in December. Photo: EPA
A
colourised computer image shows the moment the first superhot plasma
was created in a separate experiment at the Wendelstein 7-X nuclear
fusion research centre at the Max-Planck-Institut for Plasma Physics
(IPP) in Greifswald, Germany in December. Photo: EPAMeanwhile, another 1-billion-euro (US$1.12 billion) project in Germany dubbed the “stellarator” claimed last December to have achieved another milestone in the nuclear fusion quest by heating plasma to around 1 million degrees Celsius for one-tenth of a second. SCMP
MARS Has Water, Atmosphere?
NASA Admits to Unknown Objects In Space
They have tried to chase them but have failed to catch them. This video is from June 17 2007


Post a Comment Blogger Facebook Disqus