Let’s just say … it didn’t work
While
a fixture on the modern battlefield, helicopters are especially
vulnerable when hovering low to the ground and dropping off troops. For
almost 60 years, the U.S. Army and other services have tried out
different weapons to protect choppers as they land and take back off
again.
Some of these ideas
proved better than others. In November 1968, the Army’s Limited War
Laboratory began work on a huge shotgun mounted on the front of
helicopters, where it blasted out a wall of tiny bullets at anyone
unlucky enough to be on the ground.
It
didn’t work out. For one, American commanders in Vietnam—where the Viet
Cong routinely ambushed helicopters as they descended—weren’t
interested in a weapon that might kill as many friendly troops as enemy ones.
“This
system will provide troop-carrying helicopters with an immediate,
close-in … fire capability during landing and take-off in combat,”
stated the Limited Warfare Lab’s progress reports.
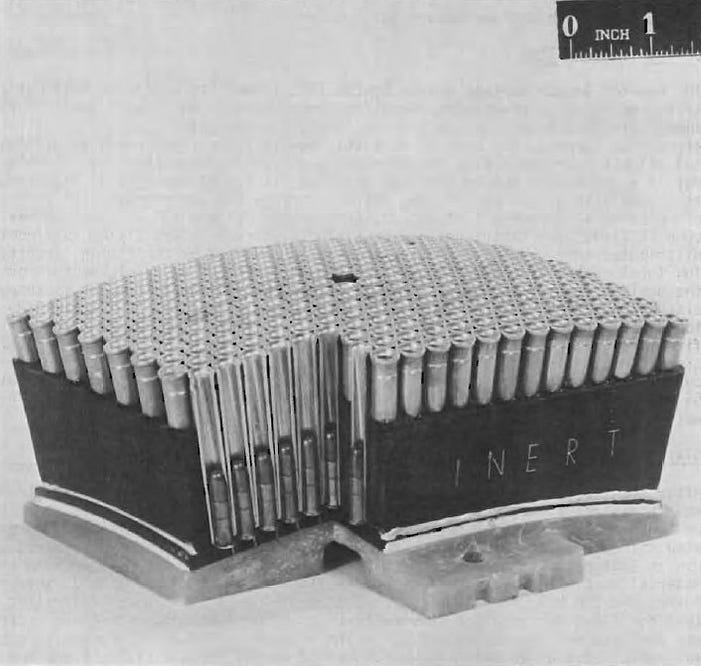
At
its core, the weapon had four clusters of .22-caliber barrels, each
pre-loaded with a single cartridge. Every one of these XM-215 “Multiple
Barrel Guns” had more than 300 separate barrels.
At the touch of a button, a crew member could fire more than a thousand rounds in 10 seconds in a 40-degree arc in front of the helicopter.
The
whole system resembled a honeycomb. But this scattergun could also
shoot its fearsome barrage at a slower pace, for up to 40 seconds of
continuous fire.
The four “modules” attached to the front of a chopper. During tests, a UH-1D Huey helicopter served as the host.
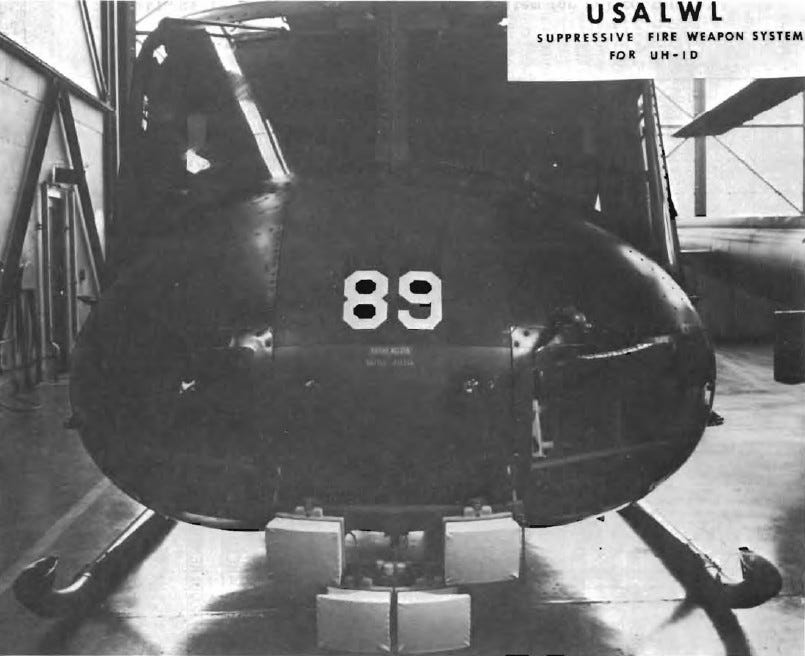

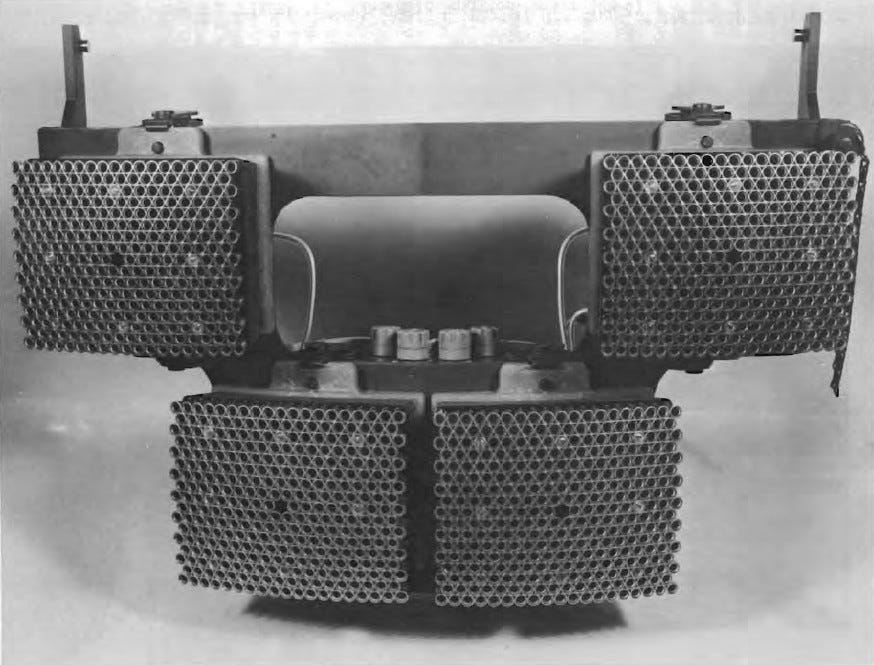
This
so-called “Suppressive Fire Weapon System for Helicopters” was the
product of years of experience—and competing viewpoints. At the time,
helicopters were still relatively new kinds of aircraft.
Five
years before the project began, the Army was debating what the military
helicopter’s proper role should be. Obviously, an attack helicopter
should carry weapons. But should a transport carry any? If so, how many?
After months of shuttling South Vietnamese troops around, most Army officials felt that only
dedicated armed gunships should get any weapons. Of 11 military
advisers to Saigon polled in 1964, only four wanted guns on transports.
The officers believed weapons would weigh down the vulnerable transport helos, making them easier prey than they already were, and further limiting the number of troops they could carry.
Army
evaluators came to the same conclusions as they tried strapping
different combinations of guns and rockets onto their rapidly expanding
chopper fleet. The service quickly abandoned plans to put four machine
guns on the front of the rotary-wing transports.
Pilots
said the mounts were too heavy and threw off their helicopters’
balance. If the weapons fired from further back on the fuselage, troops
would likely stray in front of them as they hopped out.
But it wasn’t like the alternative was much better.
The
Viet Cong were adept at ambushing defenseless helicopters as they
landed, often out of reach of the escorting gunships. American gunners
were sometimes afraid to shoot if the guerrillas got too close to
friendly soldiers.
Besides
the ambushes, insurgents filled landing zones with deadly traps.
American helicopters needed ample room to touch down—and clearances
stuck out like sore thumbs in the dense jungles.
“Possible
helicopter landing areas often are filled with bamboo stakes …
sharpened at both ends,” according to one contemporary report. “In some
cases, stakes have been wired together and mined or booby-trapped.”

The
Army responded by putting M-60 machine guns on both sides of the UH-1
Huey and CH-47 Chinook helicopters. The Chinooks also got a third gun on
their rear cargo ramp.
But
gunships were still supposed to be the primary means of beating enemy
forces back from landing zones. The slow-firing M-60s could only cover
so much ground on their own.
Enter
the Limited War Lab’s light-weight, front-mounted shotgun. In theory,
it offered a potential solution to the transport helicopters’ weight and
safety problems. With the barrage weapon loaded up, chopper crews could
pin down insurgents, drop off their troops and cargo, and then get back
into the air before taking damage.
But
the new system offered a new set of problems. The downwash from the
aircraft’s rotors risked interfering with the aerodynamics of the
small, .22-caliber bullets as they flew out of their barrels.
And while troops on board might not have been running past the barrels, the wide field of fire was still dangerous to friendlies in a tightly-packed landing zone.
Perhaps most damning, the shotgun was a single-shot weapon—or rather, a weapon that fired a lot of bullets all at once. After that, the weapon system was just dead weight. Defeating its primary purpose, it couldn’t deliver effective suppressive fire.
In
May 1971, the Army canceled the project. By that point, lab technicians
at the Aberdeen Proving Ground made four of the unique guns.
“The
anticipated request for RVN evaluation did not materialize,” is all the
progress updates have to say on the matter. RVN in this case refers to
the Republic of Vietnam, the official name of South Vietnam.
The
technicians insisted the weapons were available, if anyone was
interested. We don’t know what eventually happened to the prototypes.
But
to this very day, Army transport helicopters still rely heavily on the
same kind of side-mounted machine guns that protected their predecessors
in Vietnam. With more staying power—and fewer barrels—than the giant
shotgun.
by JOSEPH TREVITHICK. medium.com
---------------------------------------------------

Post a Comment Blogger Facebook Disqus