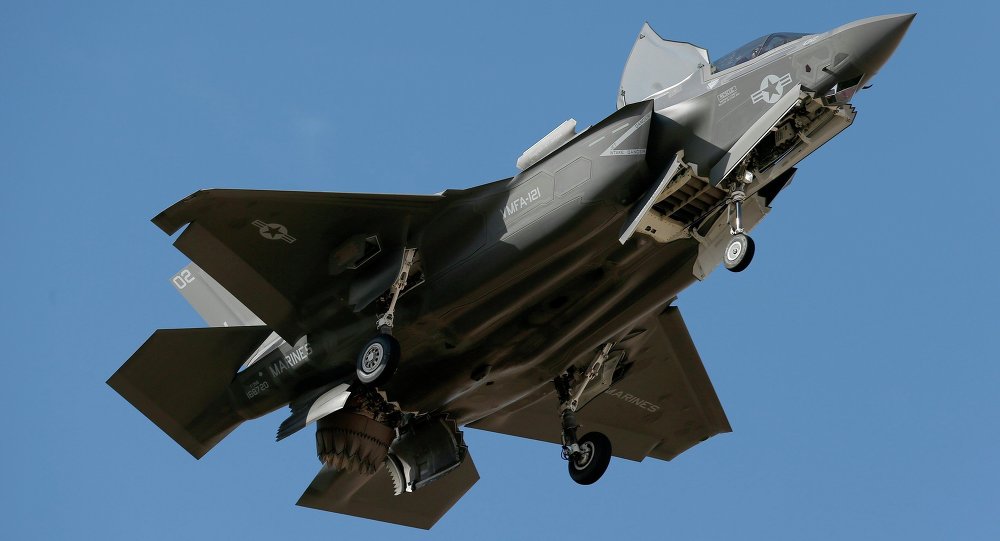
A report on the F-35 detailing years of other studies on the
stealth fighter jet says the most expensive weapons system in history is
failing, while a new plan from the US Marine Corps calls for it to be
the cornerstone of their future missions.
On Thursday, a new paper
was released by the Project on Government Oversight (POGO), an
independent nonprofit that investigates corruption, misconduct, and
conflicts of interest. In the report, Dan Grazier, a former Marine
captain and defense policy investigator at POGO, draws on reports to
outline a history of deficiencies of the F-35, which he calls a “national disaster.” 'The #F35 Is a $1.4 Trillion National Disaster: 'The only thing stealthy about it — the price tag'#lockheed #JSFhttps://t.co/BggpDgLnct— Ch. Christiaens (@chchristiaens) March 31, 2017
Grazier begins with the computer systems built into the jet,
which are supposed to gather massive amounts of data to allow the pilot
to “dominate the battlespace.” Instead, he says, they actually “interfere with the pilot’s ability to survive and prevail.”
Tests of the sensors, computers, and software have shown the systems create false targets and report false locations of targets.Grazier reported that several pilots were dissatisfied with the Distributed Aperture System (DAS), which allows them to see in any direction, including underneath the jet as well as the flight instruments and threat symbols through their $600,000 helmet systems.
Pilots called the system “operationally unusable and potentially unsafe” and reported that their targets were obscured by “symbol cluster,” which made many of them see double. Grazier says that pilots are turning the system off and choosing to rely on the traditional instrument panels instead.
“Here again, the system is little better than those it’s supposed to replace,” Grazier says.
The report also says that electronics that share data with other F-35s are creating erroneous or split images of targets, and sometimes even dropping images of targets altogether.
“All of this means that the systems meant to give the pilots a better understanding of the world around them can do exactly the opposite,” Grazier said.
Software changes only enable the jet to carry two radar-guided advanced medium-range air-to-air missiles (AMRAAMs), which are not optimized for close, visual-range combat, further diminishing its air-to-air capabilities.
Grazier also says the planes are not stealth capable, are ineffective at providing close air support, and unsuitable for carrier operations.
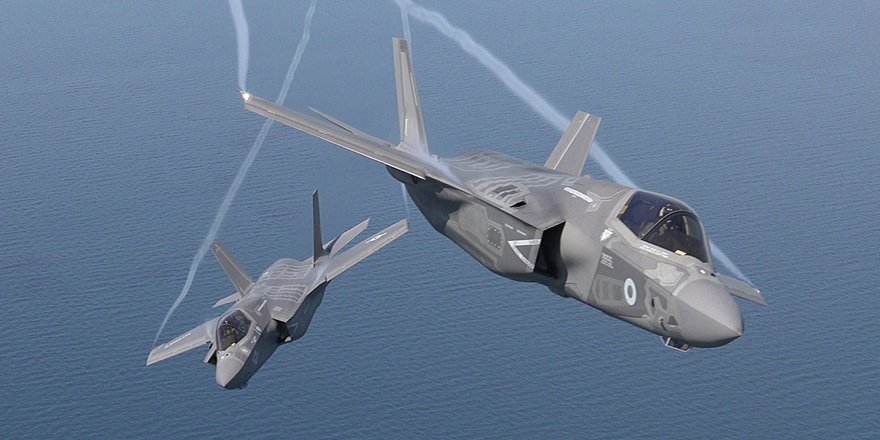

F-35 cost at $44,026 per flying hour, compare each F-16 at $20,398 per flying hour.
President Donald Trump has also questioned the program and called on Lockheed Martin to cut $600 million from the last batch of F-35s. However, this may end up costing the taxpayers more, as the F-35 that will be bought are untested and will need to be retrofitted.
The taxpayers will also have to provide additional funding for modernization, modifications, maintenance, and repair.
While the planes have not shown significant improvement over their predecessors, the Government Accountability Office (GAO) has estimated it will cost at least $3 billion to modernize the planes over the next six years.
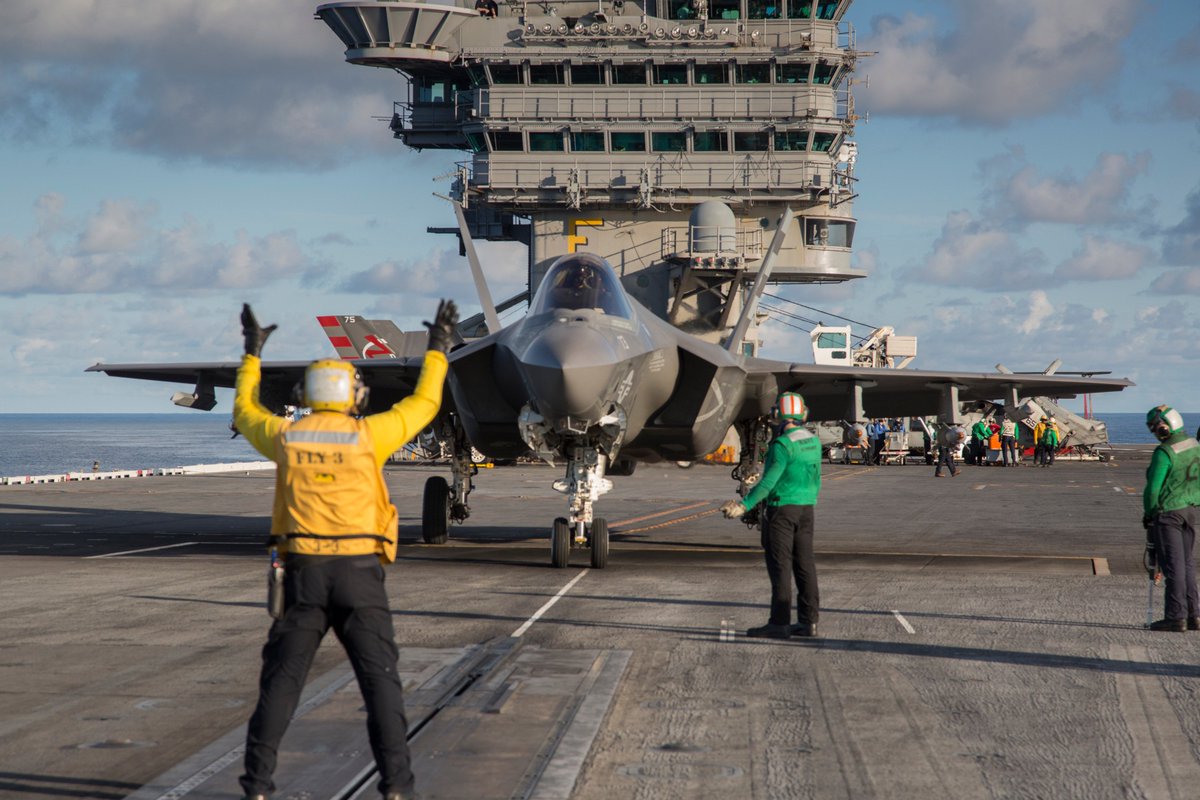

F35. Cost to bring F-35As is $119.6 million price tag, it only covers the procurement cost, does not include any of the research and development costs to develop and test the F-35A. The 2016 production-only cost for the Marine Corps’ F-35B and the Navy’s F-35C is $166.4 million and $185.2 million per plane, respectively.
At the same time, the US Marine Corp has laid out their future plans, which call for small, agile “lightning carriers” that will carry 16 to 20 F-35Bs. Most of the plan revolves around the F-35, which the Marines say will replace F/A-18, AV-8B, and EA-6B.
The plan calls for the Marine Corp to procure a total of 353 F-35s, which they say “will be the cornerstone of a multi-mission joint force.”



![Photo published for [CHINA] Pembangunan Type 075 LHD Amphibious Assault Ship telah Dimulai !!](https://pbs.twimg.com/card_img/846637280907399170/k_JfFF6N?format=jpg&name=600x314)

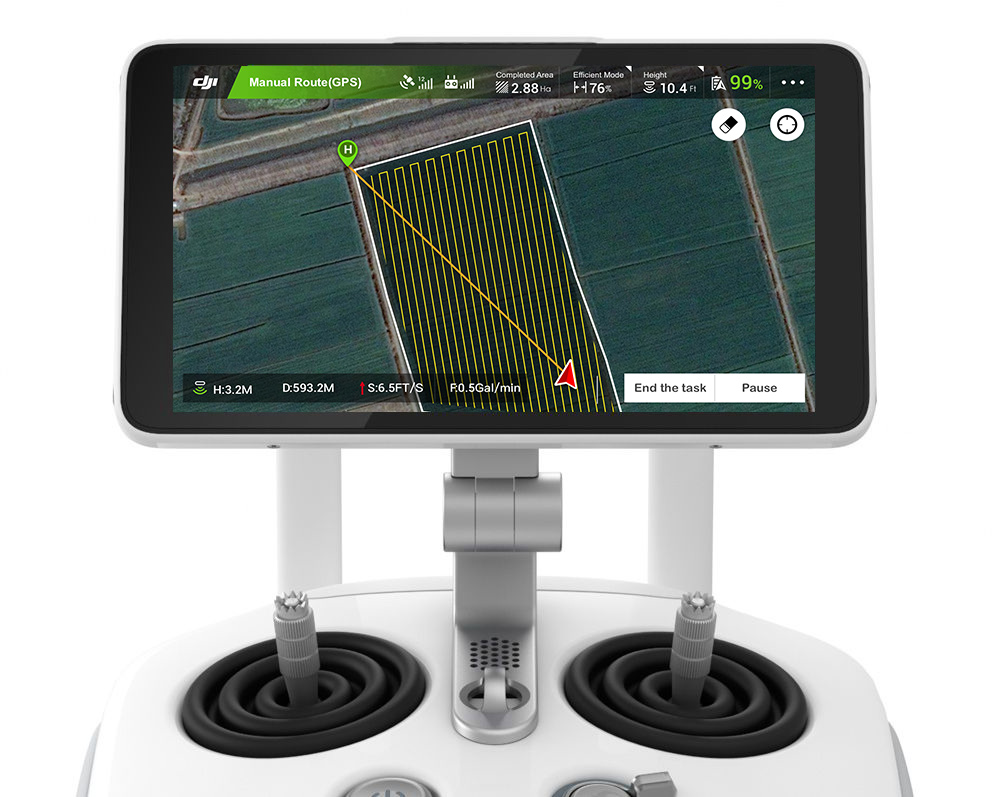



















 At a March 11 soccer game in Wuhan, police faced a new kind of threat: drones trespassing near the stadium.
On the day, police managed to safely down six active drones from up to 1 kilometer away, reports the Changjiang Daily.
At a March 11 soccer game in Wuhan, police faced a new kind of threat: drones trespassing near the stadium.
On the day, police managed to safely down six active drones from up to 1 kilometer away, reports the Changjiang Daily.

 The Silent Hunter uses a laser to zap ground and air targets up to 4
kilometers (about 2.5 miles) away, and powerful enough to cut through light vehicle armor at up to a kilometer away.
The Silent Hunter uses a laser to zap ground and air targets up to 4
kilometers (about 2.5 miles) away, and powerful enough to cut through light vehicle armor at up to a kilometer away. Battelle Drone Defender, are already used by Coalition forces in Iraq
looking to shut down ISIL quadcopters used for surveillance and grenade
attacks.
Battelle Drone Defender, are already used by Coalition forces in Iraq
looking to shut down ISIL quadcopters used for surveillance and grenade
attacks.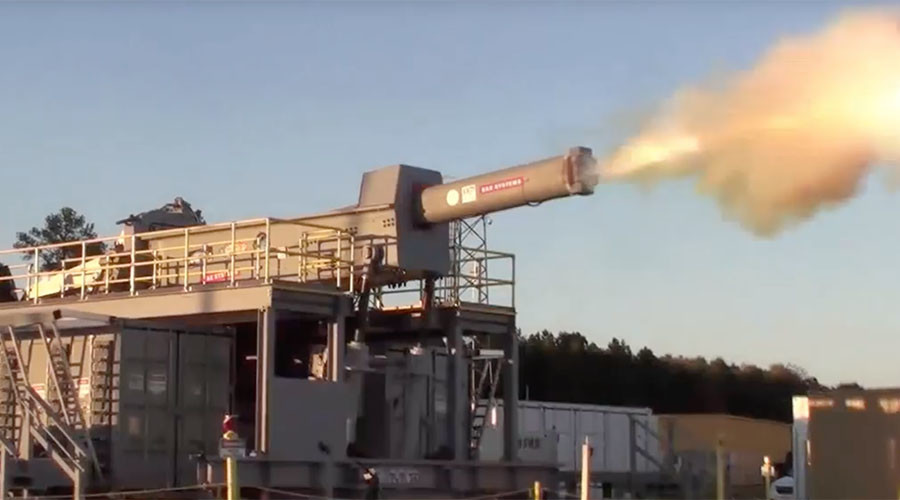

 © NASA
© NASA

















